
The RBI’s Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) conducted its monetary policy meeting from August 8 -10, 2023.
On the basis of an assessment of the evolving macroeconomic situation, the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) at its meeting today decided to:
These decisions are in consonance with the objective of achieving the medium-term target for consumer price index (CPI) inflation of 4% within a band of +/- 2%, while supporting growth.
CPI inflation picked up from 4.3% in May to 4.8% in June, driven largely by food group dynamics on the back of higher prices of vegetables, eggs, meat, fish, cereals, pulses and spices. Fuel inflation softened during May-June, primarily reflecting the fall in kerosene prices. Core inflation (i.e., CPI excluding food and fuel) was steady in June.
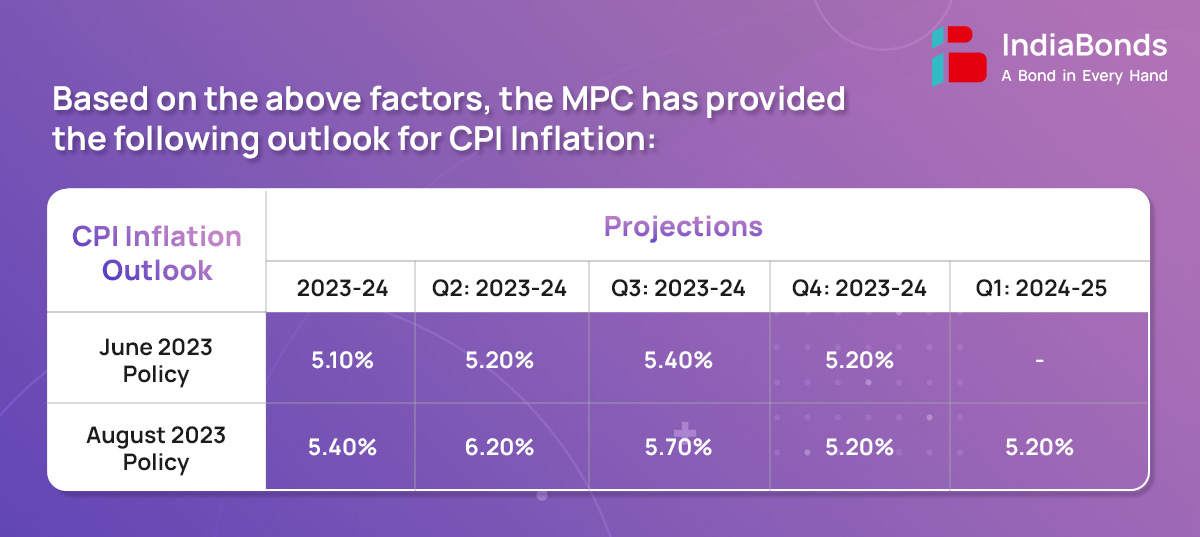
Domestic economic activity is maintaining resilience. The cumulative south-west monsoon rainfall was the same as the long period average up to 9 August 2023 although the temporal and spatial distribution has been uneven. The total area sown under Kharif crops was 0.4% higher than a year ago as on 4 August 2023. The index of industrial production (IIP) expanded by 5.20% in May while core industries output rose by 8.2% in June. Amongst high frequency indicators, e-way bills and toll collections expanded robustly in June-July, while rail freight and port traffic recovered in July after remaining muted in June. The composite purchasing managers’ index (PMI) rose to a 13-year high in July.

The global economy is slowing and growth trajectories are diverging across regions amidst moderating but above target inflation, tight financial conditions, simmering geopolitical conflicts, and geo-economics fragmentation. Sovereign bond yields have hardened. The US dollar fell to a 15-month low in mid-July on expectations of an early end to the monetary tightening cycle, although it recouped some of the losses subsequently. Equity markets have gained on expectations of a soft landing for the global economy. For several emerging market economies, weak external demand, elevated debt levels and tight external funding conditions pose risks to their growth prospects.
RBI has revise the extant regulations issued in June 2019 and put in place a comprehensive, risk-based framework for administration of financial benchmarks. The revised directions will provide greater assurance about the accuracy and integrity of financial benchmarks.
The key changes in the revised framework are: (i) withdrawal of the requirement to have a sponsor for the IDFs; (ii) allowing IDFs to finance toll-operate transfer (ToT) projects as direct lenders; (iii) permitting IDFs to raise funds through ECBs; and (iv) making tri-partite agreements optional for PPP projects.
Introduction of new framework to increase transparency for reset of interest rate on floating interest loans. Major measures taken are clearly communicate with borrowers for resetting the tenor and/or EMI and provide options for switching to fixed rate loans or foreclosure of loans.
RBI has issued several guidelines on submission of supervisory returns by supervised entities. It has been decided to consolidate and harmonize such guidelines into a single Master Direction to reduce 10 compliance burden and to promote greater ease of doing business for supervised entities.
It is proposed to (i) enable “Conversational Payments” on UPI, which will enable users to engage in conversation with AI-powered systems to make payments; (ii) introduce offline payments on UPI using Near Field Communication (NFC) technology through ‘UPI-Lite’ on-device wallet; and (iii) enhance the transaction limit for small value digital payments in off-line mode from Rs 200 to Rs 500 within the overall limit of Rs 2000 per payment instrument.
The Reserve Bank, in association with the Reserve Bank Innovation Hub (RBIH), started a pilot project in September 2022 for frictionless credit delivery through end-to-end digital processes, starting with Kisan Credit Card (KCC) loans. The pilot for KCC loans is currently operational in select districts of Madhya Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, UP and Maharashtra. Recently, dairy loans have been included in the pilot project in select districts of Gujarat. Based on the learning’s from the pilots and to expand the scope of end-to-end digital lending processes, a Public Tech Platform for Frictionless Credit delivery is being developed by the RBIH. The Platform is intended to be rolled out as a pilot project in a calibrated manner.
The next meeting of the MPC is scheduled during 4th – 6th Oct’23.
Disclaimer: Investments in debt securities/ municipal debt securities/ securitised debt instruments are subject to risks including delay and/ or default in payment. Read all the offer related documents carefully.