
In today’s day and age, there are various investment options to choose from. While some options may appear lucrative because of potential high returns, they involve potential risks to capital. For relatively lower risk – investment in NSCs and Bonds are the two most popular options. If you want to be conservative with your investments, National Savings Certificates (NSCs) and Government bonds are an ideal choice. Since they are backed by the Government of India, both are risk-free investment instruments.
As investment options with a low potential for loss, they have several advantages to offer to investors. In this blog, you will learn the difference between Bonds and NSC and understand their features and benefits.
National Savings Certificates (NSCs) are investment schemes backed by the Indian Government and issued by post offices. These are fixed-income instruments that also offer small tax benefits.
NSC investment can be done at any post office in the country in name of individual, joint holders as well as of a minor. While NSCs are a suitable investment option for investors in the small to middle-income category, they do not come with a maximum purchase limit. However, only investments up to Rs. 1.5 lakh qualify for tax deductions.




Listed below are the tax benefits available under the National Savings Certificates:
Bonds are high-security debt instruments issued by entities for raising money.
These are issued by Governments and Companies for infrastructure building or business investments. By purchasing a bond, we are effectively lending the issuer money. In exchange, they commit to repay the loan on a specified date and make periodic interest payments—typically twice a year where frequencies can be monthly, quarterly, semi-annually or annually.
There are 4 major types of bonds available in the market: fixed-interest bonds, floating-rate bonds, inflation-linked bonds and perpetual bonds. Before investing in bonds, we must understand the terminology that defines the spectrum of bonds.
Face value is the price of a single bond unit issued by a company. Nominal, principal and par value are terms used alternatively to describe a bond’s issuance price. The issuer of the bond must return the value to the investor after the maturity period.
However, we must note that a bond’s face value is not the same as its market value. Market value is the price at which the security is traded or can be currently bought/sold.
Borrowers earn interest rates on bonds throughout the investment tenure. This interest is payable periodically. Further, the interest rate is also known as the coupon rate and is decided at the time of issuance.
Tenure is the period until maturity. Bonds usually are repaid on a single fixed date which is called a bullet maturity. However, some can have staggered maturity and partially pay the principal back at regular intervals.
This refers to the borrower’s confidence in the company’s bonds to perform over the long term. Credit rating agencies – like CRISIL, CARE, ICRA – rate bonds based on the financial and balance sheet strength of the issuer.
When we include bonds in our portfolio, it could benefit us in two ways. Firstly, bonds provide us with a consistent source of income. Secondly, they help us to diversify our portfolio which may consist of other assets such as stocks, real estate, gold etc. Listed below are some primary benefits of bonds:
Bonds Investments in India as a process have progressively evolved to become simpler faster and convenient. Investors can now directly override the middlemen and invest in bonds online directly form online portals like IndiaBonds without the assistance of brokers.
You can now invest in bonds in just 3 simple steps
– Simply sign up online on www.indiabonds.com
– Complete your online KYC. It’s paperless requires no uploads and digitally verifies you, all in under 3 minutes.
– You are now set to invest in the bonds of your choice online! Choose through a wider variety of bonds both from primary and secondary markets to invest from. That’s about it.
To read a step wise detailed explanation read our blog on How to Invest in Bonds.
If you are still unsure of which bond to invest in, use IndiaBonds’ Bond for you Tool. This tool assists investors set their financial goals and curates a list of bonds that would complement their investment requirements keeping their goals in mind.
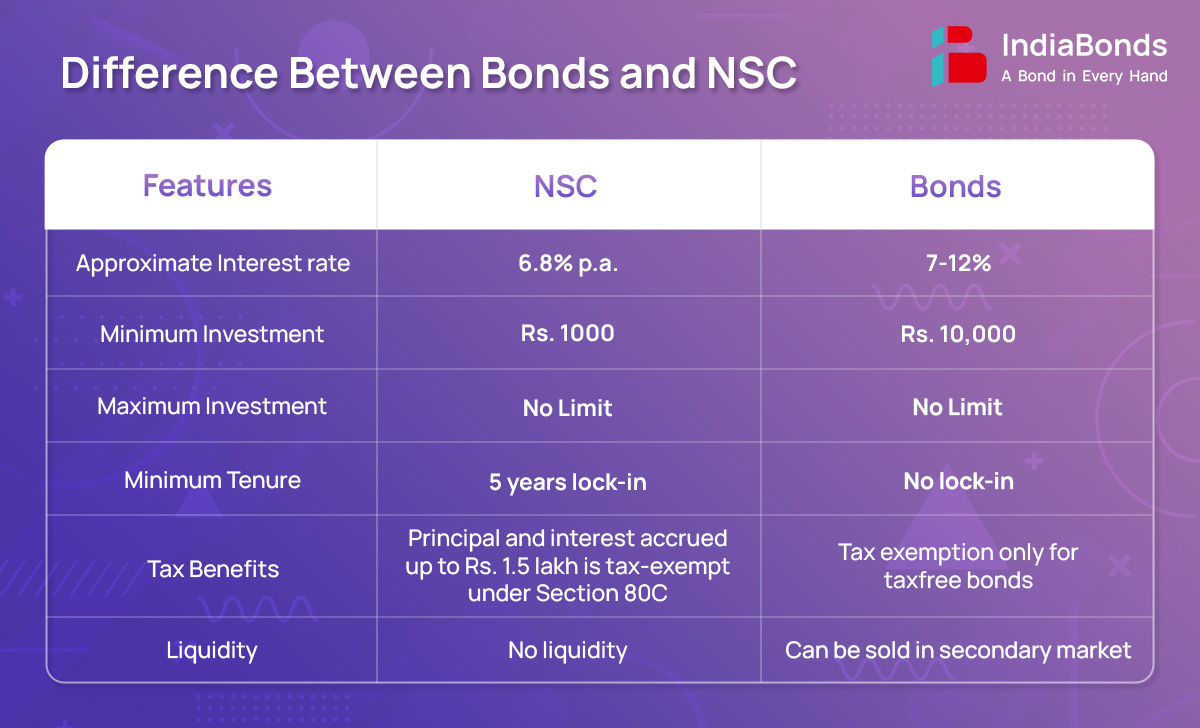
National Savings Certificates are government issued instruments and are more for small income category where people have little access or knowledge on investments. Bonds offer a much wider choice in terms of returns as well as tend to be much more liquid/traded.
NSC accounts can’t be closed before five years have passed unless one or all account holders in a joint account expires.
Under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act, investments up to 1.5 lakhs are tax-deductible.
You can apply for an NSC account transfer at your current or desired post office branch. Moreover, for a Joint A or B account, all account holders’ signatures are required on the application.
An NSC account can be opened with as little as Rs 1,000. Deposits in excess of Rs. 100 in multiples of Rs. 100. There is no maximum investment limit.
Disclaimer: Investments in debt securities/ municipal debt securities/ securitised debt instruments are subject to risks including delay and/ or default in payment. Read all the offer related documents carefully.